





 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
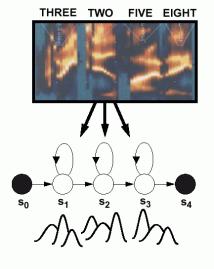
| • | Acoustic models
encode the |
||||||||||||||
| temporal
evolution of the |
|||||||||||||||
| features
(spectrum). |
|||||||||||||||
| • | Gaussian mixture
distributions |
||||||||||||||
| are used to
account for |
|||||||||||||||
| variations in
speaker, accent, |
|||||||||||||||
| and
pronunciation. |
|||||||||||||||
| • | Phonetic model
topologies are |
||||||||||||||
| simple
left-to-right structures. |
|||||||||||||||
| • | Skip states
(time-warping) and |
||||||||||||||
| multiple paths
(alternate |
|||||||||||||||
| pronunciations)
are also |
|||||||||||||||
| common features
of models. |
|||||||||||||||
| • | Sharing model
parameters is a |
||||||||||||||
| common strategy
to reduce |
|||||||||||||||
| complexity. |
|||||||||||||||